Physic
IGE built-in 3D physics engine is an integration of the Bullet Physic, which is a 3D physic engine.
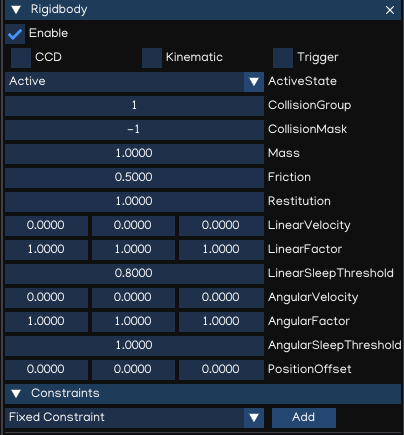
Rigidbody
In physics simulation, rigid bodies enable physics-based behaviour such as movement, gravity, and collision. A Rigidbody is the main component that enables physical behaviour for a game object.
With a Rigidbody attached, the object will immediately respond to gravity. If one or more Collider components are also added, the game object is moved by incoming collisions.
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
CCD |
Enable/disable Continous Collision Detection mode |
Kinematic |
Set Rigidbody to Kinematic or Dynamic mode |
Trigger |
Enable trigger collision events |
ActiveState |
Set activation state |
CollisionGroup |
Collision group value |
CollisionMask |
Collision mask value |
Mass |
The mass of the object (in kilograms by default). |
Friction |
Friction value |
Restitution |
Restitution value (aka bounciness value) |
LinearVelocity |
Linear velocity |
LinearFactor |
Linear factor |
LinearSleepThreshold |
Linear sleeping threshold |
AngularVelocity |
Angular velocity |
AngularFactor |
Angular factor |
AngularSleepThreshold |
Angular sleeping threshold |
PositionOffset |
Position offset (adjust the center of the physic object) |
Constraints |
List of constraints applied in Rigidbody |
Note
If the game object contains Rigidbody component, it’s Transform will be controlled by the Rigidbody. Thus, to change the transform just apply force or torque to the Rigidbody by using Python Script.
Note
When Trigger is enabled, use Python Script to receive triggered events. Refer to Rigidbody API for more details.
Collision
To configure collision between game objects, you need to use Colliders. Colliders define the shape of the game object for the purposes of physical collisions.
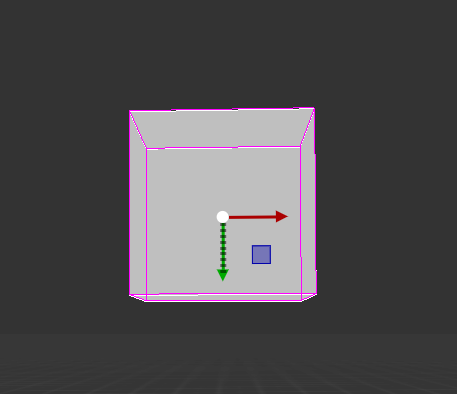
BoxCollider
The BoxCollider is a basic cuboid-shaped collision primitive, which are useful for items such as crates, chests, or floors using thin boxes.
It can also be used to create complex collision shape using CompoundCollider component.
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
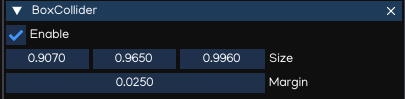
Size |
Size of the collider in X, Y, Z direction |
Margin |
Collision margin |
Note
Collision margin is used to optimize physic calculation, should keep it larger than 0.
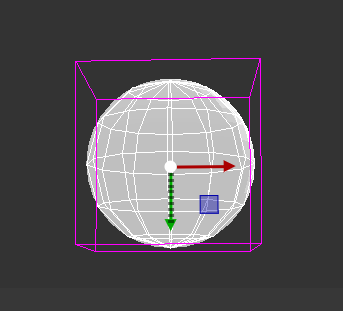
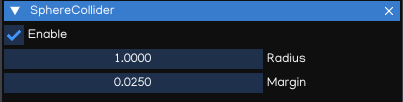
SphereCollider
The SphereCollider is a basic sphere-shaped collision primitive.
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Radius |
The radius of the sphere shape |
Margin |
Collision margin |
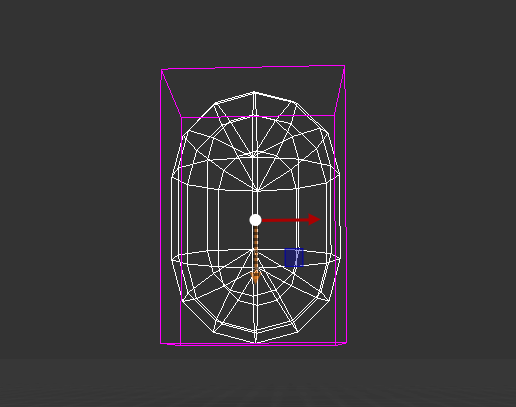
CapsuleColider
The CapsuleCollider is made of two half-spheres joined together by a cylinder, to create a capsule primitive shape.
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Height |
The total height of the collider |
Radius |
The radius of the collider width |
Margin |
Collision margin |
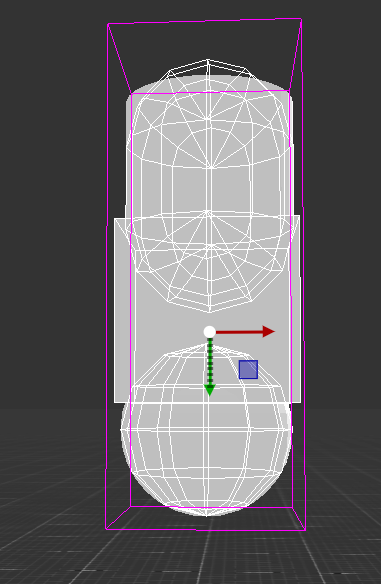
CompoundCollider
Compound colliders approximate the shape of an object while keeping a low processor overhead, by combining primitive colliders of the child objects. When you create a compound collider like this, you should only use one Rigidbody component, placed on the owner object in the hierarchy.
Note
CompoundCollider do not work with child objects which contains other CompoundCollider or MeshCollider.
Note
Should have only one Rigidbody attached to the whole hierarchy which the root object contains both CompoundCollider and Rigidbody. Otherwise, the simulation may not work as designed.
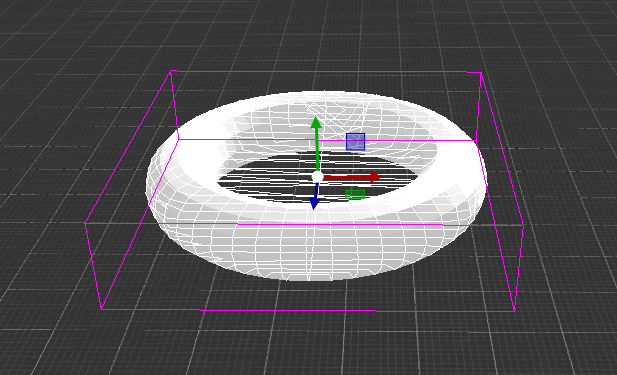
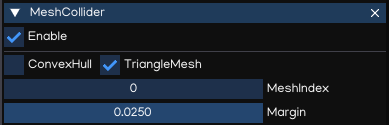
MeshCollider
The MeshCollider create Collider from meshes in FigureComponent. It is more accurate for collision detection than using primitives colliders.
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
ConvexHull |
Create and convex hull from mesh |
TriangleMesh |
Use the triangle mesh |
Margin |
Collision margin |
Note
Using MeshCollider results in higher processing overhead than primitive colliders, so it is best to use MeshColliders sparingly.
Note
Using TriangleMesh is only allowed if the Rigidbody is Kinematic.
Constraints
A constraint is used to connect a Rigidbody to another Rigidbody or a fixed point in space. Constraints apply forces that move rigid bodies, and limits restrict that movement.
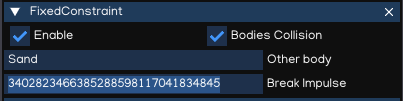
FixedConstraint
FixedConstraint restricts an object’s movement to be dependent upon another object. The best scenarios for using them are when you have objects that you want to easily break apart from each other, or connect two object’s movement without parenting.
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Bodies Collision |
Enable/disable collision between linked bodies |
Other body |
Other Rigidbody or Softbody component |
Break Impulse |
The force that needs to be applied for this constraint to break. |
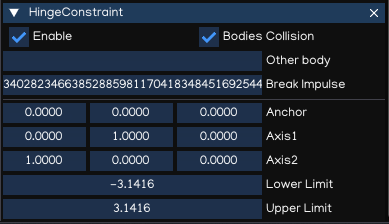
HingeConstraint
The HingeConstraint groups together two Rigidbodies, constraining them to move like they are connected by a hinge.
It is perfect for doors, but can also be used to model chains, pendulums, etc…
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Bodies Collision |
Enable/disable collision between linked bodies |
Other body |
Other Rigidbody or Softbody component |
Break Impulse |
The force that needs to be applied for this constraint to break |
Anchor |
The position of the axis around which the body swings, in local space |
Axis1 |
Rotation around Z |
Axis2 |
Rotation around X |
Lower Limit |
The lowest angle the rotation can go |
Upper Limit |
The highest angle the rotation can go |
SliderConstraint
A SliderConstraint allows a object controlled by Rigidbody to slide along a line in space, like sliding doors, for example.
Property
Function
Bodies Collision
Enable/disable collision between linked bodies
Other body
Other Rigidbody or Softbody component
Lower Limit
Lower limit of the slider
Upper Limit
Upper limit of the slider
SpringConstraint
The SpringConstraint joins two Rigidbodies together but allows the distance between them to change as though they were connected by a spring.
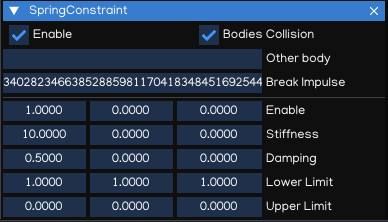
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Bodies Collision |
Enable/disable collision between linked bodies |
Other body |
Other Rigidbody or Softbody component |
Enable |
Enable/disable spring on X, Y, Z axis |
Stiffness |
Spring stiffness in X, Y, Z axis |
Damping |
Amount that the spring is reduced when active |
Lower Limit |
Lower limit of the distance range over which the spring will not apply any force |
Upper Limit |
Upper limit of the distance range over which the spring will not apply any force |
Dof6SpringConstraint
Dof6SpringConstraint incorporate all the functionality of the other constraint types and provide greater customization.
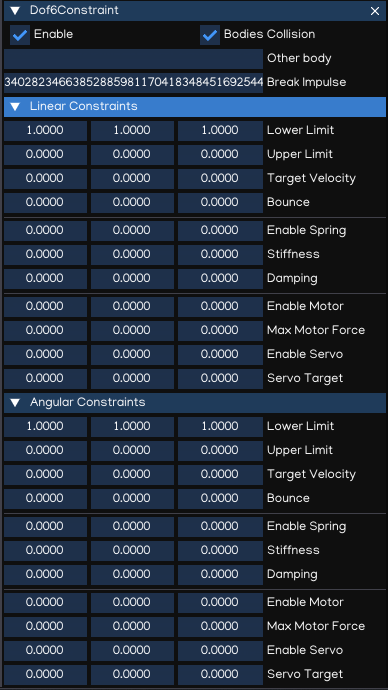
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Bodies Collision |
Enable/disable collision between linked bodies |
Other body |
Other Rigidbody or Softbody component |
Lower Limit |
Lower limit of the axis |
Upper Limit |
Upper limit of the axis |
Target velocity |
Target velocity |
Bounce |
Bounciness |
Enable Spring |
Enable/disable spring |
Stiffness |
Spring stiffness value |
Damping |
Spring damping value |
Enable Motor |
Enable/disable motor |
Max Motor Force |
Max motor force |
Enable Servo |
Enable/disable Servo |
Servo Target |
Servo target |
The first 3 dof axis are linear axis, which represent translation of rigidbodies, and the latter 3 dof axis represent the angular motion. Each axis can be either locked, free or limited.
For each axis:
Lowerlimit == Upperlimit -> axis is locked.
Lowerlimit > Upperlimit -> axis is free.
Lowerlimit < Upperlimit -> axis is limted in this range.
Check Bullet Physic manual document for more information.
Softbody
The soft body dynamics provides rope, cloth simulation and volumetric soft bodies, on top of the existing rigid body dynamics. The Softbody component works with FigureComponent, it manipulates Figure meshes to simulate deformable objects like cloth, fluid, jelly,…
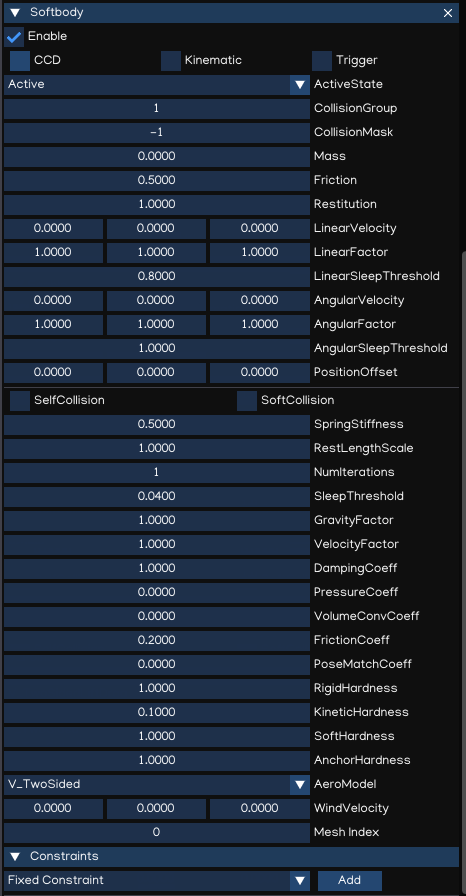
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
CCD |
Enable/disable Continous Collision Detection mode |
Kinematic |
[Ignored] Softbody is Dynamic object as alway. |
Trigger |
Enable trigger collision events |
ActiveState |
Set activation state |
CollisionGroup |
Collision group value |
CollisionMask |
Collision mask value |
Mass |
The mass of the object (in kilograms by default). |
Friction |
Friction value |
Restitution |
Restitution value (aka bounciness value) |
LinearVelocity |
Linear velocity |
LinearFactor |
Linear factor |
LinearSleepThreshold |
Linear sleeping threshold |
AngularVelocity |
Angular velocity |
AngularFactor |
Angular factor |
AngularSleepThreshold |
Angular sleeping threshold |
PositionOffset |
[Ignored] Use mesh data without offset |
SelfCollision |
Enable/disable collision between parts of the shape |
SoftCollision |
Enable/disable soft collision |
SpringStiffness |
Spring stiffness value |
RestLengthScale |
Scale resting length of all springs |
NumIterations |
Positions solver iterations (pIterations) |
SleepThreshold |
Sleeping threshold |
GravityFactor |
Gravity factor |
VelocityFactor |
Velocities correction factor (kVCF) |
DampingCoeff |
Damping coefficient value (kDP) |
PressureCoeff |
Pressure coefficient value (kPR) |
VolumeConvCoeff |
Volume conversation coefficient [kVC] |
FrictionCoeff |
Dynamic friction coefficient (kDF) |
PoseMatchCoeff |
Pose matching coefficient (kMT) |
RigidHardness |
Rigid contacts hardness (kCHR) |
KineticHardness |
Kinetic contacts hardness (kKHR) |
SoftHardness |
Soft contacts hardness (kSHR) |
AnchorHardness |
Anchors hardness (kAHR) |
AeroModel |
Aerodynamic model (default: V_Point)
|
WindVelocity |
Wind velocity for interaction with the air |
Constraints |
List of constraints applied |
Softbody also works with all type of Constraints, together with Rigidbodies or other Softbodies.
Check Bullet Physic manual document for more information.
PhysicManager
The PhysicManager is automatically created and attached to the root object, to have the global setting of the Physic system.
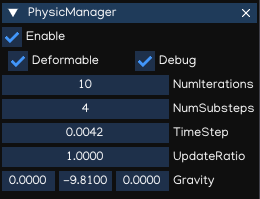
Property |
Function |
|---|---|
Deformable |
Enable/disable physic with Softbody simulation |
Debug |
Show Physic debug |
NumIterations |
Number of iterations per frame |
NumSubsteps |
Number of substeps. If NumSubSteps > 0, interpolate motion between fixedTimeStep |
TimeStep |
Fixed time step value (default: 1/60) |
UpdateRatio |
Update ratio, useful to do slow motion effect |
Gravity |
Global gravity value |
Please refer to Bullet Physic Manual and Python API Document document for more details of Physic usage using IGE.